Leading Automotive, Telecom and ITS companies successfully carry out first Cellular V2X trial in Japan
- Continental, Ericsson, Nissan, NTT DOCOMO, OKI and Qualcomm Technologies join forces to successfully perform cellular V2X trial as announced beginning of the year
- Direct and network-based communications between vehicles, to the infrastructure and to vulnerable road users tested under varying conditions
- Continental evaluates results as promising for the use of C-V2X for future mobility use cases
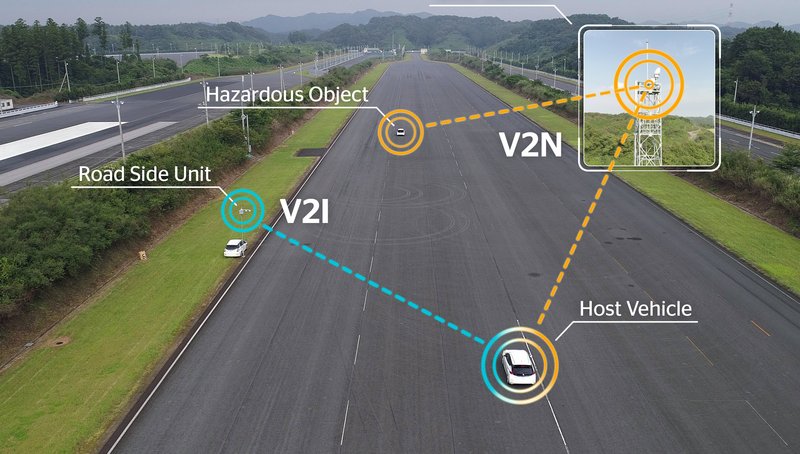
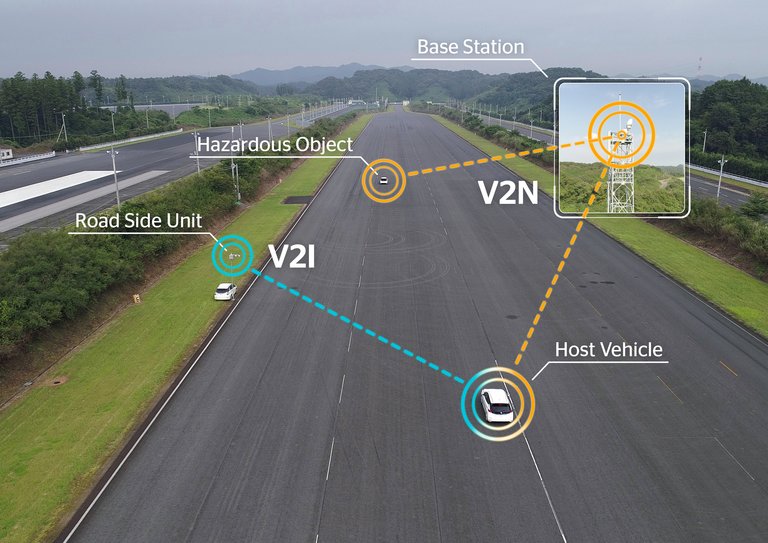
Yokohama, 13 December 2018. Continental announced today the completion of a joint Cellular V2X trial in Japan together with Ericsson, Nissan, NTT DOCOMO, OKI and Qualcomm Technologies. The companies have successfully conducted Japan’s first C-V2X testing in the country using 5.8 GHz as the experimental radio frequency for direct communication. The use cases were designed to address various aspects of V2X communication, such as Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V), Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) and Vehicle-to-Pedestrians (V2P) direct communications, as well as Vehicle-to-Network (V2N) operations. With a combination of direct and network-based communications between vehicles, infrastructure, and vulnerable road users, such as pedestrians and cyclists, the test results showed that C-V2X can exploit the full potential of connected and intelligent mobility. In addition, the tests also indicated the technology’s strengths for reliability and latency, which assists in enabling the communication of mission critical messages quickly and efficiently. Direct communication provides vehicle to vehicle (V2V), vehicle to infrastructure (V2I) and vehicle to pedestrian (V2P) and other vulnerable road users connectivity even in the most remote areas where no mobile coverage is available. Under mobile coverage, C-V2X is designed to also enable a vehicle-to-network (V2N) communication link to deliver cloud-based exchanges of information over a longer range, including information on upcoming road conditions or traffic situations
Tested under varying conditions
In their field trials, the companies focused on sending messages directly via cellular V2X technology (PC5). The use cases were tested under varying conditions to evaluate the C-V2X basic communications performance. With test vehicles passing each other at speeds of up to 110 kilometers per hour and with a truck or even buildings blocking the communications both direct and network-based communications were tested.
The companies observed a mean latency of 20 milliseconds for direct communication and a nearly error-free communication even at longer distances such as 1.2 kilometers with unobstructed line-of-sight condition as measured by the C-V2X test system. With these results, the companies demonstrated the performance capabilities of C-V2X. The direct communication technology used in the tests was based on the 3GPP Release 14 specifications.
The companies also demonstrated a wide area V2N communication with end to end average communication latency of 50 milliseconds in NTT DOCOMO’s commercial network in the connected mode state.
The trials took place in multiple test tracks in Japan, where the performance of C-V2X was tested using five scenarios – Do Not Pass Warning, Electronic Emergency Brake Lights, Hazardous Location Warning, Intersection Movement Assist and Vulnerable Road User Warning. These were chosen, to ensure that basic aspects of the communication technology were considered. Thus, the tests did not only focus on V2V communication but also on V2I, V2P and V2N communication under different traffic situations and driving speeds.
Promising test results achieved
For the trial, Continental used the Qualcomm® 9150 C-V2X Reference Design, which features the Qualcomm® 9150 C-V2X chipset with integrated Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) capability to build connected car systems and to integrate the systems into Nissan test vehicles. Working with Qualcomm Technologies, Nissan made a test driving plan for C-V2X to be used during the trials at the proving grounds. Bringing in their expertise in roadside unit (RSU) infrastructure and applications, OKI demonstrated V2I as a viable technology for advanced traffic applications by integrating the Qualcomm® 9150 C-V2X chipset into their RSU. Ericsson, as one of the leading companies in the technology and service for telecommunication, assisted in testing the V2N use case scenario, combining direct communication and LTE-A network technologies. NTT DOCOMO provided a LTE-A network and V2N applications to demonstrate the benefits of the complementary use of network-based communications for a variety of advanced automotive informational use cases.
Following the positive test results Continental will continue to further develop and investigate the C-V2X technology, globally as well as in Japan to enable an early global deployment. C-V2X will most likely be implemented initially on the 4.5 G (or LTE Advanced Pro) and further on 5G mobile communication standards from 2022 onwards.
“The test trials in Japan have once again confirmed, that cellular V2X communication is well suited to transmit information quickly and reliably between vehicles, the infrastructure and other road users. The possibility to communicate directly as well as via the cellular network dramatically enhances the vehicle’s visibility and enables additional cloud services for the connected and intelligent mobility of the future”, says Johann Hiebl, Head of the Continental business unit, Infotainment & Connectivity.
About C-V2X
C-V2X is a global solution for V2X communications designed to support improved automotive safety, automated driving and traffic efficiency, and is a V2X communication technology compliant with the global 3GPP specifications. C-V2X is composed with direct communication and network-based communication. C-V2X complements Advanced Driver Assistance Systems sensors, such as cameras, radar and Light Detection or LiDAR. C-V2X direct communication mode is firstly specified in 3GPP Release 14 and designed to offer vehicles low latency communications for V2V, V2I and V2P without the involvement of a cellular network, or cellular network subscription, by operating on a designated and harmonized 5.9 GHz ITS spectrum. Network-based communication offer wide area communications for V2N services. Currently, 3GPP is working on further enhancements of C-V2X in 5G.

Sebastian Fillenberg
Head of External Communications
AUMOVIO